March 06, 2023
ChatGPT vs. Google Bard: What are the differences?
Author:

CSO & Co-Founder
Reading time:
11 minutes
The global generative AI market is predicted to reach an outstanding $100.8 billion by 2030, up from $7.9 billion in 2021, growing at a CAGR of 34.3%. [1] Not so long ago, generative AI models like ChatGPT and Google Bard were a thing of science-fiction movies. It wasn’t until just recently, in 2014, with the development of GANs, that AI models could generate increasingly authentic content. [2]
In 2020, OpenAI released ChatGPT – the latest and largest model in the GPT series. In the first two months of operation, the model had already garnered 100 million active users. [3] In a bid to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market, Google recently announced the release of its own model to compete with ChatGPT – Google Bard.
With two large, sophisticated language models on the market, it’s easy to wonder which among them will come out on top. This article will provide a comprehensive ChatGPT vs. Google Bard comparison, citing their differences, strong points, and weaknesses. We’ve also thrown in some information on how to use Google Bard and ChatGPT.
Addepto empowers businesses with a game-changing AI Text Analysis Tool for document analysis.
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is the third model in the GPT (generative pre-trained transformer) series and one of the largest language models in the world. The language model was developed by OpenAI, the company responsible for DALL.E.
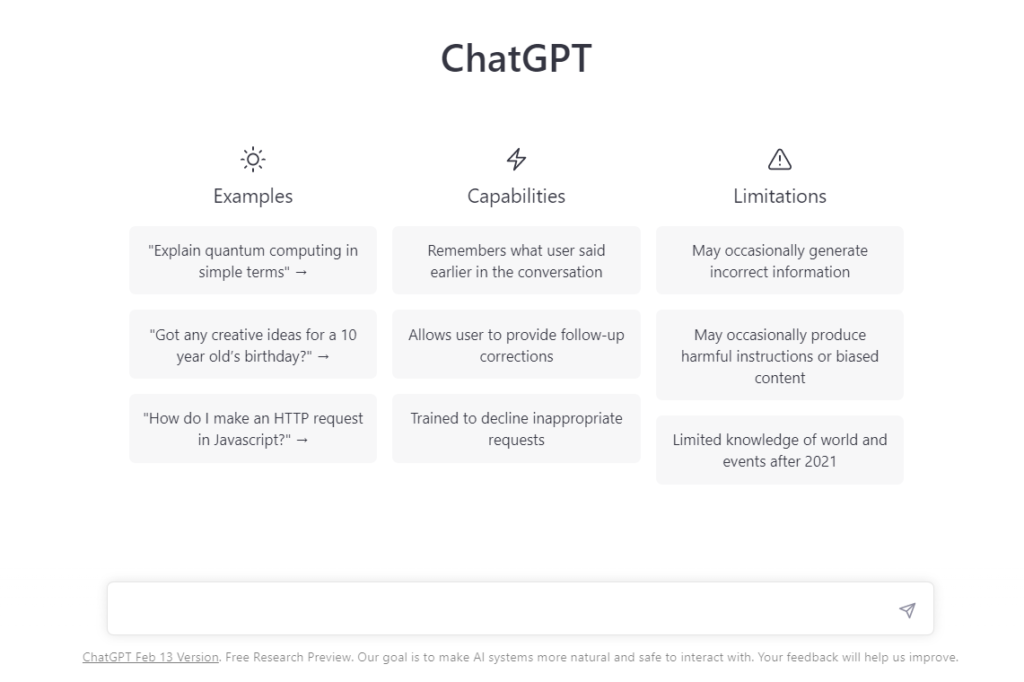
ChatGPT was trained on a massive dataset and featured 175 billion parameters, making it one of the largest language models on the market. It works by using neural networks to process user input and generate human-like responses. This gives it a unique range of capabilities, including the ability to answer questions factually, provide recommendations, answer questions, and even write engaging stories and essays.
These capabilities also give ChatGPT many potential applications, particularly in education, customer service, entertainment, and mental health support.
However, despite being such a powerful tool, ChatGPT like any other AI language model, has certain limitations. Here are some important considerations:
- Lack of real-world understanding: ChatGPT does not possess true understanding or knowledge of the world. It generates responses based on patterns and information present in its training data, but it does not have personal experiences or a genuine comprehension of concepts.
- Sensitivity to input phrasing: The way a question or prompt is phrased can significantly affect the model’s response. ChatGPT is sensitive to slight changes in wording and may provide different answers based on those variations.
- Prone to factual inaccuracies: While ChatGPT has been trained on a vast amount of data, it can still generate incorrect or inaccurate information. It’s always advisable to verify important facts from reliable sources.
- Tendency to be verbose or overuse certain phrases: ChatGPT may sometimes provide excessively long or verbose responses. It may also overuse certain phrases or exhibit repetitive behavior, which can reduce the overall quality of the conversation.
- Lack of context between turns: ChatGPT processes text on a per-turn basis and does not have a memory of the entire conversation. Consequently, it may occasionally provide inconsistent or contradictory responses within the same dialogue.
- Difficulty handling ambiguous queries: When faced with ambiguous queries or ambiguous pronouns, ChatGPT might make assumptions or guess the user’s intention, which can lead to incorrect or confusing answers.
- Potential biases in responses: ChatGPT reflects the biases present in its training data. Despite efforts to mitigate biases, the model can still exhibit biased behavior or respond to sensitive topics inappropriately.
It’s important to exercise critical thinking when interacting with AI models, validate information from reliable sources, and be aware of these limitations to make the most informed judgments.
It might be interesting to you: How can you use ChatGPT in business?
What is Google Bard?
Google Bard is a conversational AI service meant to function similarly to ChatGPT. The model was unveiled on 6th February 2023 and is expected to be made available to the public in the near future.
The model is powered by Google’s Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA), which, like GPT-3, was built on a transformer model. [4] However, unlike the GPT series, which relies on training data to generate responses, Google Bard sources all its output data directly from the internet. This makes it especially suitable for applications where users need up-to-date information.
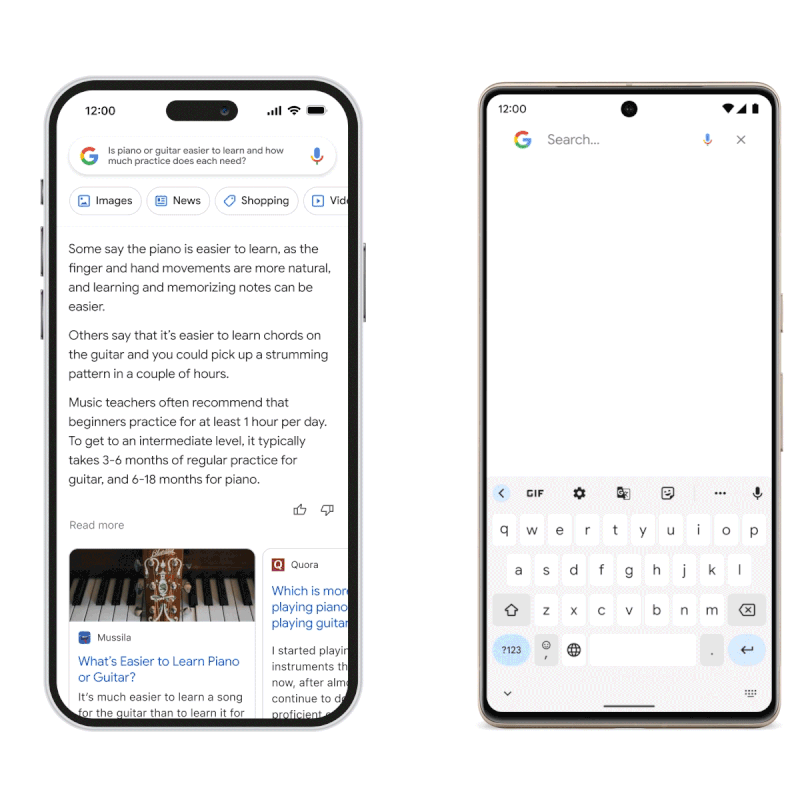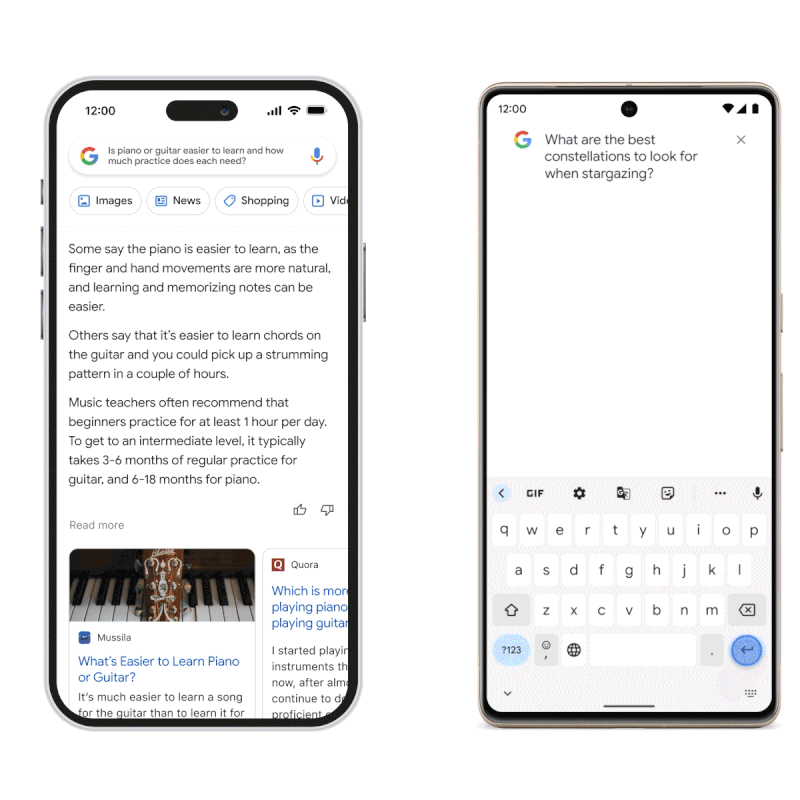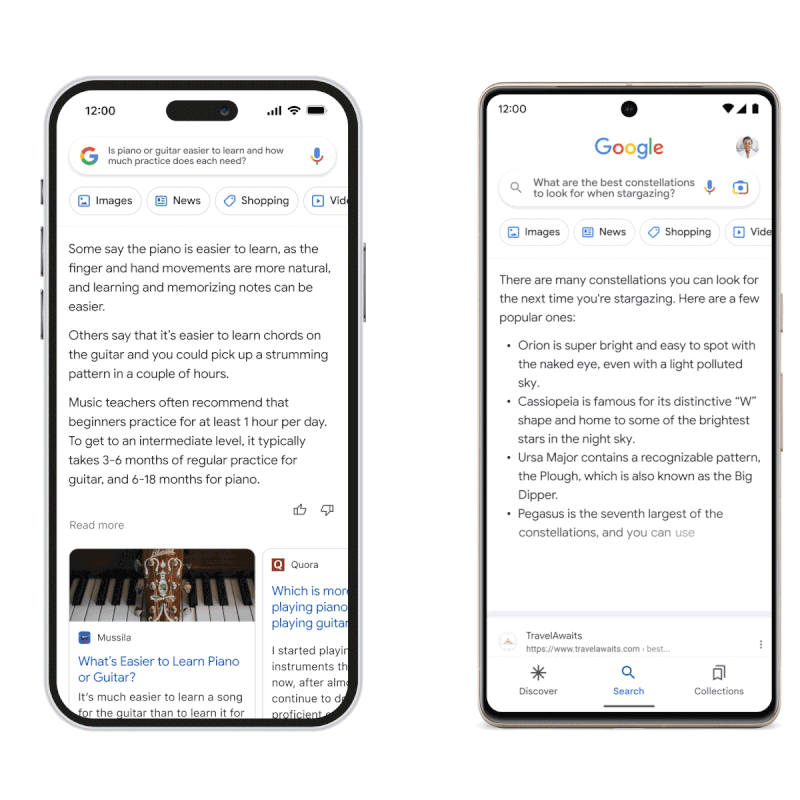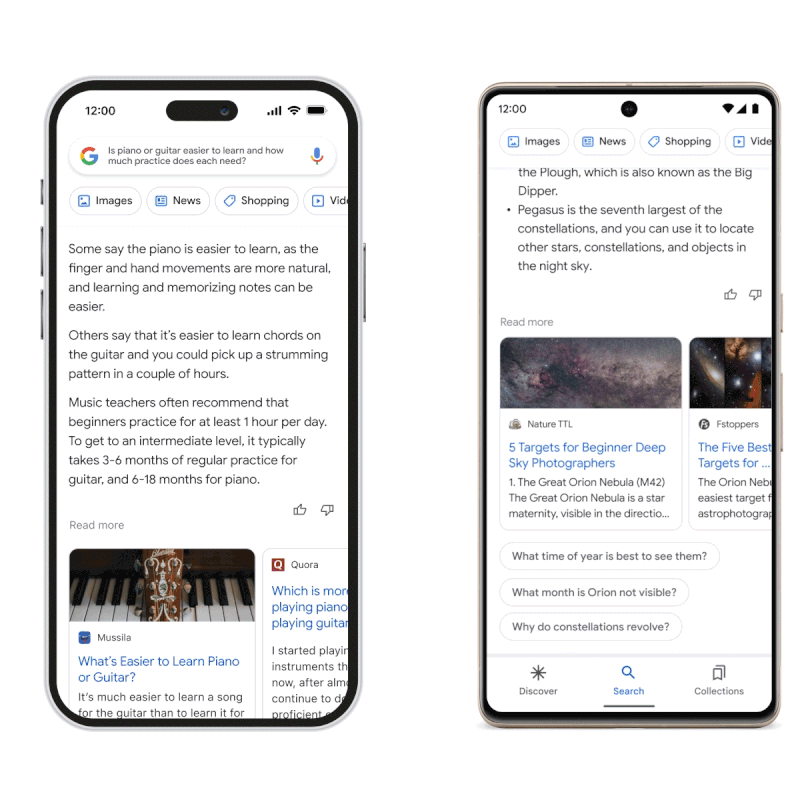
Source: blog.google
On the downside, Google Bard has a pretty rough unveiling, where it answered a question incorrectly. However, since it’s still in development, it might get more factual as developers iron out the kinks.
Google Bard has a broad application potential, but it lacks some of the capabilities demonstrated by ChatGPT, including the ability to write stories and essays. Instead, this model is primarily geared towards simplifying google searches by augmenting results and presenting answers in a conversational way.
What’s the difference between Google Bard and ChatGPT?
Sure, Google Bard and ChatGPT have a lot of similarities. They answer questions in a conversational manner and make internet searches much easier. However, they have a lot of differences as well. Everything from their operational framework to how they source their data sets them apart. Here are some of the most notable differences between the two.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Price and availability
ChatGPT has been around for more than two years. It first started out as a free model, but OpenAI recently announced a paid version, where users pay $20 for priority access and faster speeds.
There’s still not much information about Google Bard’s monetization, but there’s a large possibility that the model may remain free for some time after being made public.
Currently, Google Bard is only available to a small team of trusted testers, who will test its efficiency and accuracy before releasing it to the public. Conversely, ChatGPT already has a lot of public users, and it’s still scaling up.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Accuracy
ChatGPT has a pretty impressive record for producing factual answers. Unfortunately, there’s still a considerably high number of instances where the model generates incorrect or biased answers. Additionally, ChatGPT is limited to pre-2021 information that predates its training data. This means that the model can provide answers or offer recommendations based on current events.
Conversely, Google Bard sources all its data in real time from the internet. This gives it a much higher chance of providing information that is in line with current trends and recent discoveries. Unfortunately, the model had a pretty rough unveiling when it answered a question incorrectly.
During the unveiling, someone asked Google Bard to answer the question, “What new findings from the James Webb Space Telescope can I tell my 9-year-old about?” In response, the model provided an answer consisting of three bullet points, one of which stated that the James Webb telescope took the first photos of a planet outside the solar system.
This information is incorrect since, according to NASA, the first photographs of an exoplanet were taken in 2004 – decades before the James Wedd telescope was released.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Features
Both models have relatively similar features. As conversational AI models, they enable you to input queries, then provide the most feasible output based on available data. Both models also allow you to make follow-up questions or start a new chat on a different topic.
In regards to question answering, Google Bard has the upper hand since it provides a greater context to answers based on recent data. However, ChatPT outclasses it in the number of use cases based on its features.
Unlike Google Bard, ChatGPT can generate a wide range of text, including articles, essays, product descriptions, and much more. It can also generate code when provided with enough information.
It wouldn’t be far-fetched to assume that Google Bard may have some of these features, but we’ve not seen them demonstrated or even talked about by the people responsible for its development.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Integration Capabilities
The monetization and profitability of both models rely heavily on their integration capabilities into other systems. Take ChatGPT, for example. The model has already seen widespread integration into various Microsoft products like Edge, Bing, and Teams.
Google also recently announced an updated version of GPT-3.5, which will power Bing. This upgrade will allow users to interact with the search engine conversationally rather than querying the search engine box. There’s also talk that ChatGPT may also be integrated into Opera Browser. [5]
According to Google, its AI chatbot will be integrated into its search engine. Like ChatGPT and Bing, Google Bard will allow users to search queries through the chatbot rather than having to use the traditional search bar. Google also announced that it would give third-party developers access to the chatbot, so it might see a broader range of use cases.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Interface
Creating a chatbot that is easily approachable by diverse users requires a strong emphasis on user-friendliness and interface design. When comparing Bard to ChatGPT, it becomes evident that Bard holds a distinct advantage in this regard. Bard boasts a visually appealing interface that enhances the overall user experience, with well-structured and easily scannable formatted text.
Notably, Bard allows users to modify their questions even after they have been posed, adding a layer of flexibility to the interaction. Additionally, Bard enables users to express their feedback by upvoting or downvoting responses, as well as conducting web searches for further information.
As a result, Bard’s interface exudes a sense of cleanliness and organization, contributing to an enhanced user experience.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT: Delivering images in response
Although ChatGPT excels at producing comprehensive textual responses, it lacks the ability to deliver images as part of its output. This could be attributed to OpenAI’s focus on other properties like Dall-E, which specialize in generating images. On the other hand, Google Bard possesses the capability to include images within its text responses.
How to use ChatGPT and Google Bard
ChatGPT is publicly available. To use it, you need to visit OpenAI’s website, click on ChatGPT, create an account, and you’re good to go. You only need your email address and mobile number to create a free account.
Conversely, Google Bard is not yet available to the public. However, a few people have gotten the chance to use the AI’s beta version. You can check whether it’s available on your phone by opening Google App and checking whether you see a chatbot option.
Both language models have the same basic principle of operation. You simply have to type in a query, and the chatbot will respond accordingly. However, you may need to get a bit more detailed and specific to get your desired results.
Final thoughts
Generative AI is changing how we do research and generate content. Google Bard and ChatGPT show the highest potential for application across numerous fields. They have relatively similar features, except for a few differences that make them uniquely suitable for specific applications.
Unfortunately, Google Bard isn’t yet available to the public, so most of the information about its capabilities and use cases is mainly speculative.
It is important to note that the field of generative AI is rapidly evolving, and new advancements are being made at a remarkable pace. While Google Bard may not be accessible to the public currently, it is conceivable that it will become available in the future, introducing a new era of possibilities in content generation. As we eagerly anticipate the potential wider release of Google Bard, it is worth keeping an eye on the latest developments and updates in the field of generative AI.
In the meantime, ChatGPT continues to be a powerful tool that has already showcased its capabilities in various domains. Its ability to generate comprehensive text responses has proven invaluable to researchers, writers, and content creators alike. With ongoing research and improvements, it is foreseeable that future iterations of ChatGPT and other generative AI models will bridge the gap in delivering both text and multimedia outputs.
As we navigate this transformative era of generative AI, it is essential to stay informed and adapt to the ever-evolving landscape. Exploring resources like our Generative AI Development process can provide valuable insights into the current state of the technology and its potential future advancements. By embracing the possibilities of generative AI, we can unlock new horizons in research, creativity, and content generation.
References
[1] Acumenresearhandconsulting.com. Generative AI Market. URL: https://bit.ly/3YiwCpW. Accessed March 03-2023
[2] Techtarget.com. Generative AI. URL: https://bit.ly/41N9CSQ. Accessed March, 03-2023
[3] Businessofapps.com. ChatGPT Statistics. URL: https://bit.ly/3EZkjbo. Accessed March 03-2023
[4] Zdnet.com. Bard Builds on Conversational Lamda Bot that Engineer Had Called Sentient. URL: https://www.zdnet.com/article/googles-bard-builds-on-controversial-lamda-bot-that-engineer-had-called-sentient/. Accessed March 03, 2023
[5] Toms.guide.com. Opera ChatGPT. URL: https://www.tomsguide.com/news/opera-chatgpt. Accessed March 03, 2023
Category: