March 12, 2025
What is Image Annotation?
Author:

CSO & Co-Founder
Reading time:
3 minutes
Computer vision is transforming industries by enabling machines to interpret and analyze visual data. From facial recognition to autonomous vehicles, these advancements rely on one crucial process: image annotation. This foundational step ensures that machine learning models can accurately identify and classify objects in images, improving their predictive capabilities.
But what exactly is image annotation, and why is it so important? This guide explores its definition, key techniques, and real-world applications across industries like healthcare, security, agriculture, and robotics.
Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- Image annotation is essential for training computer vision models to recognize, classify, and analyze objects accurately.
- Different annotation types include image classification, object detection, segmentation, and boundary recognition.
- Techniques such as bounding boxes, polygon annotation, and masking help refine model accuracy.
- Image annotation powers applications in healthcare, security, agriculture, robotics, and self-driving cars.
What is Image Annotation?
Image annotation is the process of labeling images to train machine learning models for computer vision. It enables AI to detect and classify objects accurately, powering applications like facial recognition and autonomous vehicles.

Why Image Annotation Matters
Machine learning models require high-quality training data to make accurate predictions. Annotated images provide labeled datasets, helping AI recognize patterns and improve over time. The better the annotation, the more precise the model’s performance.
Types of Image Annotation
Image Classification
Labels an image based on its overall content (e.g., “dog” or “car”), but does not specify object location.
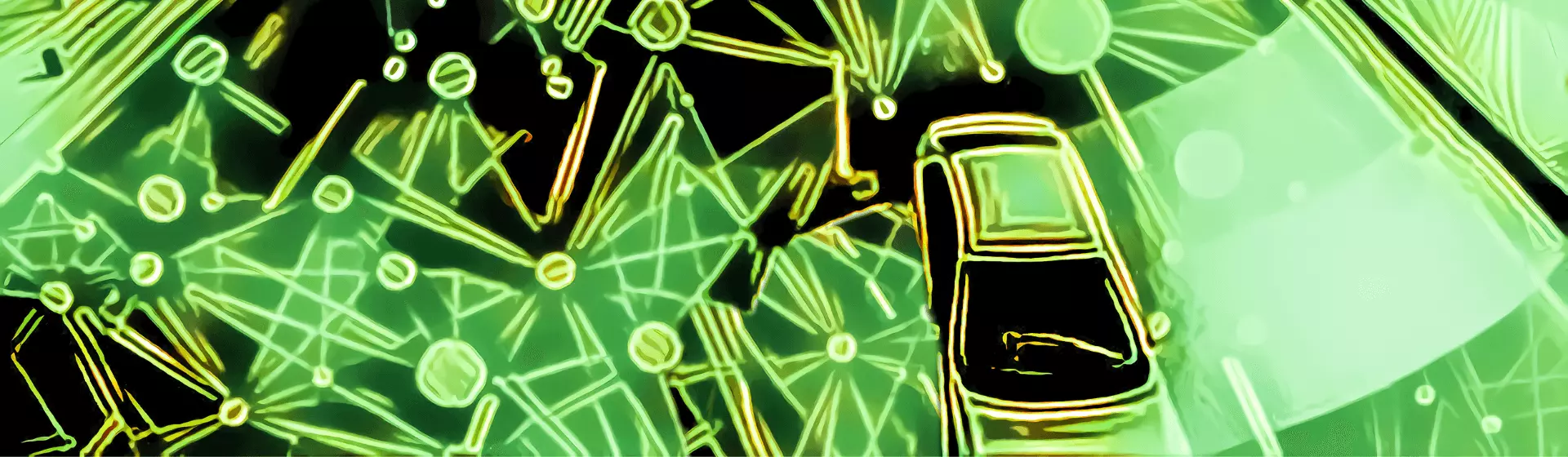
Objection Detection/Recognition
Object detection trains the machine model to accurately detect different types of objects noticeable in the natural setting. It identifies whether an object exists, where it is located, and the number of items in an image. Object detection can also help your machine to identify various objects in non-annotated images on its own.
 Source: cloudfactory.com
Source: cloudfactory.com
Segmentation
Breaks images into regions to differentiate objects. Includes:
- Semantic segmentation: Groups similar objects together (e.g., all cars as one entity).

- Instance segmentation: Identifies individual objects within the same category.
- Panoptic segmentation: Combines both for detailed object identification.

Boundary Recognition
Trains models to detect edges and outlines, essential for self-driving cars and medical imaging.
Image Annotation Techniques
1. Bounding Boxes
Rectangles around objects, commonly used for object detection.
2. Polygon Annotation
Outlines irregularly shaped objects, improving accuracy.
3. Landmarking
Marks key points, useful for facial recognition and pose estimation.
4. Masking
Highlights relevant image areas while hiding others.
5. Polyline Annotation
Defines linear features like roads and power lines.
6. Tracking
Labels and follows objects across video frames.

Source: cogitotech.com
Real-World Applications
- Facial Recognition: Unlocks devices and enhances security systems.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Helps self-driving cars detect pedestrians, roads, and traffic signs.
- Healthcare: Assists in diagnosing diseases by labeling medical images.
- Agriculture: Detects plant diseases and monitors crop health.
- Wildlife Conservation: Tracks animal populations and detects environmental changes.
Final Thoughts
Image annotation is crucial for AI-driven advancements in multiple industries. By understanding its types, techniques, and applications, businesses can leverage this technology for improved automation and decision-making.
Category:





